Profile
surveying: -
Profile levelling is generally adopted to find
elevation of points along a line such as for road, rails or rivers etc. In this
case, readings of intermediate stations are taken and reduced level of each
station is found. From this cross section of the alignment is drawn.
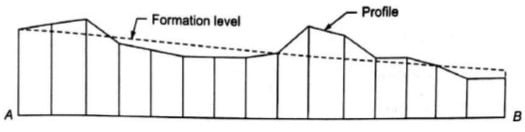
Formation Road Level:-
The Formation Level is
the level at which excavation ceases and construction commences. It
is the lowest point of the path structure. It is the prepared ground on which
the sub base layer is laid.
Rise and fall formula.
For (B.S to I.S)
Rise = IF (B.S>I. S, (B.S-I. S), (0))
Fall = IF (B. S<I.S, (I.S-B. S), (0))
For (I.S to I.S)
Rise = IF (I. S1>I.S2, (I. S1-I. S2), (0))
Fall= IF (I. S1<I.S2, (I. S2-I. S1), (0))
For (I.S to F.S)
Rise= IF (I.S>F. S, (I.S-F. S), (0))
Fall= IF (I. S<F.S, (F.S-I. S), (0)
CONTOUR: -
Contouring in surveying is the
determination of elevation of various points on the ground and fixing these
points of same horizontal positions in the contour map.
Types of Contour Lines in Surveying and their Importance
1.
Isopleth
Isopleth
on a contour map connects the places having the same value of some measurable
quantity of geographical or meteorological phenomena.
For Ex. The population density
of an area can be calculated by the quotient of population in the area and
surface area of a region.
2. Isohyet
Isohyet
indicates the points of equal rainfall of an area in the given time.
3. Isobar
Isobars
on contour maps indicates the point of equal or constant atmospheric pressure
for a given period.
This
type of contour is used in the prediction of future weather patterns isobars
are commonly used in television weather reporting.
4.
Isobaths
It
is a type of imaginary contour lines on a map of chart that connects all the
points having same depth below water surface like ocean, sea and lake.
Terrain contour: -
When the terrain is
generated by lifting the grid points, the limits of the terrain by the minimum rectangle that contains the plan
projection of all contour curves.
Types of terrain contour
·
Plain terrain. For slope, 0 – 10*
·
Rolling terrain. For slope, 10 – 60*
·
Mountainous terrain & hilly. For slope, > 60*
CULVERT: -
A small bridge having
total length of 6 m or less than 6 m between the faces of abutments is known as
culvert. Culvert is a permanent drainage structure mainly constructed to carry
roadway or railway track over small streams or channels.
Types of Culverts: -
Following are the types of culverts
generally used in construction:
1.
Box Culvert (Single or Multiple)
The culvert consisting of
one or more numbers of rectangular or square openings, having their floor and
top slabs constructed monolithic ally with abutments and pier, is known as box culvert.
2.
Arch stone
Culvert
A pipe arch culvert is a round culvert reshaped to allow a lower
profile while maintaining flow characteristics. It is good for installations
with shallow cover. Materials used for arch culverts are RCC, Corrugated Metal
or Stone Masonry.
3. Slab culvert
The culvert, having its
superstructure consisting of RCC slab which carries the bridge floor, is known as slab culvert.
4. HPC- Hume pipe culvert.
The culvert which consists of one or more pipes
placed side by side over a concrete base below the embankment of a roadway or
railway track is known as pipe culvert.
Drainage Slope: -
All of your drain pipe (with one
exception) must slope slightly downhill. Usually 1/8" per foot
is plenty for drainage, this is the same as the commonly recommended
1% slope.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter span link in the comment box.